HVAC&R Mechanical Engineering
Where problem-solvers thrive.
What is HVAC&R?
HVAC&R stands for Heating, Ventilation, Air Conditioning, and Refrigeration. It is a technology used to control the indoor environment of buildings, ensuring comfortable temperatures, proper airflow, high-quality air and food safety. HVAC&R systems are widely used in residential, commercial, and industrial settings to maintain optimal conditions for occupants, protect sensitive equipment and food.
HVAC&R systems consume a large amount of energy, still primarily from fossil fuels, which contributes to greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, the refrigerants used in HVAC&R systems can be potent greenhouse gases themselves if not properly managed. As a result, there is a growing emphasis on developing more energy-efficient HVAC&R technologies and transitioning to a carbon neutral energy sources.
Why this concentration at Cal Poly?

Heating, ventilation, air-conditioning and refrigeration plays a crucial role in maintaining indoor air quality, thermal comfort, and energy efficiency in buildings. With the increasing demand for sustainable and energy-efficient solutions, professionals with expertise in HVAC&R are highly sought after to help reduce carbon emissions and minimize environmental impact.
- Cal Poly's HVAC&R concentration is the gold standard for the best hands-on education for a career in the HVAC&R industry.
- The lab intensive courses use state-of-the art equipment and will teach you how to apply the basic principles of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics and heat transfer to design and implement energy-efficient HVAC&R technologies.
- Small class size, dedicated top expert professors, an inclusive and equitable environment, a focus on your success, industry support, real life senior design projects with industry advisors, and a strong alumni network are just a few of the benefits you can expect from our HVAC&R concentration.
Mechanical Engineering at Cal Poly is...
What can you do with a HVAC&R concentration?

HVAC engineers work in a variety of settings, including engineering firms, construction companies, government agencies, and facilities management departments.
They are also in high demand in industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and energy.
HVAC engineers may choose to specialize in certain areas, such as sustainable design or building automation systems, and their expertise is essential in ensuring efficient and comfortable indoor environments.
Additionally, another career option is to work as a sales engineer, promoting and selling HVAC&R equipment to manufacturers and businesses.

Refrigeration engineers usually work in the commercial and industrial sectors.
They are responsible for designing, installing, and maintaining refrigeration systems in large-scale facilities such as supermarkets, warehouses, and manufacturing plants.
These professionals ensure that the temperature and humidity levels are properly regulated to preserve perishable goods and maintain optimal working conditions.
Additionally, refrigeration engineers play a crucial role in ensuring energy efficiency and reducing environmental impact by implementing sustainable cooling solutions.
Student Projects
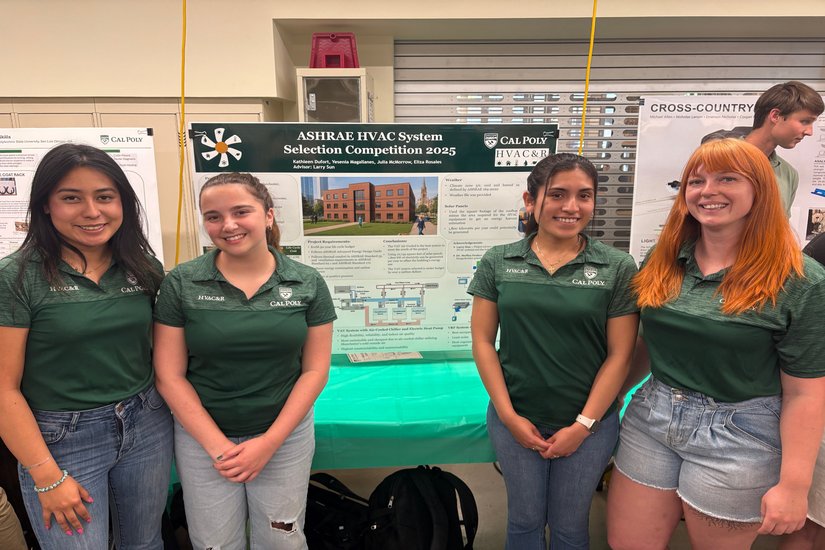
HVAC System Design for a Medical Office in Manchester, England
For this ASHRAE Student Design Competition project, students were challenged to select an optimized HVAC system for a new three-story medical office building in Manchester, England. The team evaluated three system options—two VAV systems with reheat (paired with water- or air-cooled chillers) and a VRF system with heat recovery and dedicated outdoor air system (DOAS). Using tools like DesignBuilder and HVAKR for energy modeling and load analysis, the team considered life cycle cost, maintainability, indoor air quality, and energy efficiency. Ultimately, the recommended solution was a VAV system with reheat, an air-cooled chiller, and an electric heat pump—balancing long-term performance and budget while meeting stringent ASHRAE standards for healthcare environments.
Developing a Load Calculation Lab for ME 3355: Hands-On HVAC&R Learning at Cal Poly
This project supports the transition to semesters by creating a new load calculation labs for ME 3355, a course focused on the fundamentals of HVAC&R systems. Working with industry-standard software platforms like DesignBuilder/EnergyPlus and HVAKR, students developed a three-part lab series exploring building envelope modeling, zoning, and sensitivity analysis and the differences between the radiant time series and heat balance methods. Exercises include analyzing the impact of design conditions such as weather location, insulation values, and infiltration rates on peak heating and cooling loads. Through this hands-on lab experience, future students will gain practical insight into real-world HVAC&R system sizing, helping bridge the gap between theory and application in building energy performance.
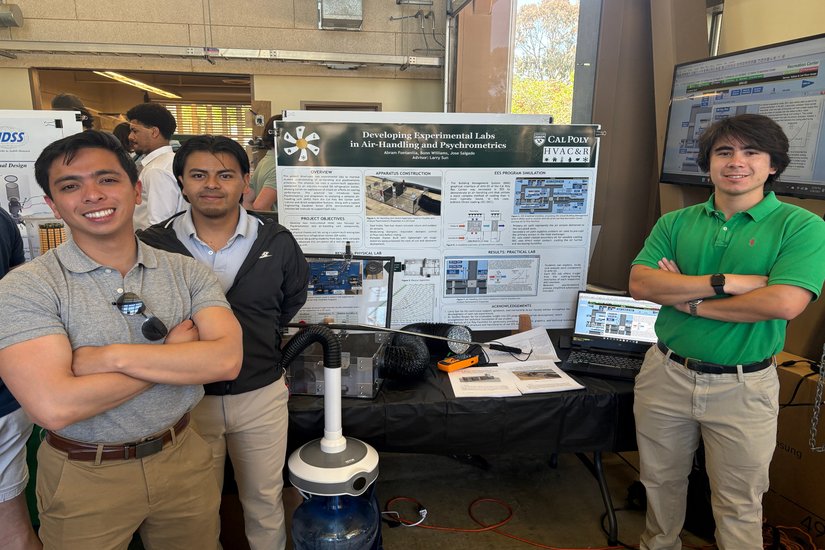
Enhancing HVAC&R Education Through Experimental Psychrometric Labs
This project focuses on improving student understanding of air-handling systems and psychrometric processes through two newly developed lab experiences for ME4456. In the physical lab, students use a custom-built air-mixing apparatus connected to a DX refrigeration trainer to measure and observe mixed air conditions and their affect on cooling coil performance. The practical lab explores a real-world air-handling unit at the Cal Poly Recreation Center, modeled using Engineering Equation Solver (EES) software. This virtual lab walks students through indirect/direct evaporative cooling processes and simulates a building management system (BMS) interface. Together, these labs provide a hands-on and analytical foundation for applied psychrometrics and HVAC&R concepts.
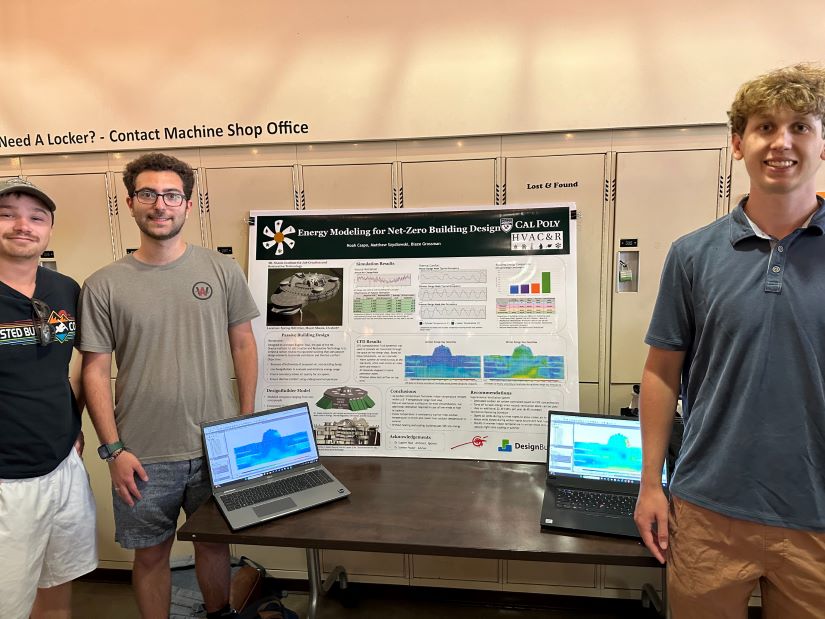
Senior Design – Energy Modeling for Net-Zero Building Design
Guided by the visionary design of architect Eugene Tssui, the Mt. Shasta Institute for Job Creation and Restorative Technology will be a carbon-neutral, multipurpose building that incorporates passive design elements for natural ventilation and thermal comfort. Our HVAC&R senior design students contributed by evaluating the effectiveness of the proposed net-zero building design, applying energy modeling to reduce energy consumption, ensuring appropriate indoor air quality, and leveraging underground temperatures to maintain consistent thermal comfort. This project highlights our commitment to educate students on sustainable technology in modern building design.